基本语法 注释 单行:#
多行:'''或"""
1 2 3 4
变量类型 查看类型 type()查看变量类型
isinstance(a, (类型1, ...))判断是否是其中一种类型或子类
数字
int
bool(True/False)
float
complex(复数)
/返回浮点数,//返回整数的部分
字符串 单行字符串可用''或"",多行字符串可用''' '''或""" """
转义符号\
不让\生效,在引号前加r
可用+连接字符串,*重复字符串
字符串是不可改变量
切片
左闭右开
-1为末尾位置
还可加上步长,步长-1表示逆向
格式化
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 print ("我叫 %s 今年 %d 岁!" % ('小明' , 10 ))'aaa' print (f'Hello {name} ' ) 'name' : 'baidu' , 'url' : 'www.baidu.com' }print (f'{w["name" ]} : {w["url" ]} ' )
列表 列表的元素是可改变的
1 2 3 4 5 6 a = [1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 ]print (a[1 : 2 ]) print (a[1 :]) 1 ] = 0 print (a)
列表操作
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 1 , 2 , 3 ]4 )print (list1) del list1[0 ]print (list1) import operator1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 ]1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 ]print (operator.eq(list1, list2))
元组 元组的元素不可以改变
可以把字符串看成特殊的元组
1 2 3 4 5 tup = (1 , ) 1 ) print (type (tup)) print (type (a))
集合 集合的元素可变,唯一
创建可用{}或set(),空集合要用set
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 a = set ('abracadabra' )set ('alacazam' )print (a)print (a - b) print (a | b) print (a & b) print (a ^ b)
字典 创建可用{}或dict,空字典可用{}创建
key必须为不可变类型(数字、字符串、元组、布尔等)
1 2 3 4 a = {'a' : 1 , 'b' : 2 , 'c' : 3 , 4 : 'd' }print (a) print (a['a' ]) print (a[4 ])
字典操作
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 : 1 , 2 : 2 , 3 : 3 }del d[1 ]print (d) print (d)
输入输出 1 2 3 4 5 6 input ("Enter price: " )print (price)print (price, end = '' )
format格式化
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 print ("Hello, {}!" .format ("Alice" ))print ("Hello, {0}, you are {1} years old." .format ("Bob" , 25 ))print ("Site name: {name}, Rank: {rank}" .format (name="Google" , rank=1 ))"name" : "Alice" , "age" : 18 }print ("Name: {0[name]}, Age: {0[age]}" .format (user))"site" : "Google" , "rank" : 1 }print ("Site: {site}, Rank: {rank}" .format (**data))
格式化控制符
格式符
含义
示例值
示例结果
d十进制整数
{0:d}42
f浮点数(默认 6 位)
{0:f}3.141593
.2f保留 2 位小数
{0:.2f}3.14
>10右对齐,占 10 宽度
{0:>10} text
<10左对齐,占 10 宽度
{0:<10}text
^10居中,占 10 宽度
{0:^10} text
,千位分隔符
{0:,}1,000,000
%百分比(乘以 100)
{0:.2%}25.00%
条件/循环
导入模块 导入模块的搜索路径:
当前目录
环境变量 PYTHONPATH 指定的目录
Python 标准库目录
.pth 文件中指定的目录
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 import sysfrom sys import argv, pathfrom sys import *
每个模块都有一个__name__属性
如果模块是被直接运行,__name__ 的值为 __main__。
如果模块是被导入的,__name__ 的值为模块名。
数学函数
abs(): 绝对值
ceil()/floor(): 向上/向下取整
round(): 四舍五入
cmp(): 比较两个数
max()/min(): 取最大/最小值
pow(): 开方
sqrt(): 平方根
错误异常 处理异常
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 try :except ExceptionType1:except ExceptionType2 as e:else :finally :
抛出异常
1 2 3 4 def sqrt (x ):if x < 0 :raise ValueError("不能对负数开平方" )return x ** 0.5
常见异常类型
异常名
说明
ValueError参数类型/值不合法
ZeroDivisionError除以 0
IndexError索引超出范围
KeyError字典中键不存在
FileNotFoundError打开的文件不存在
TypeError操作/函数类型不对
NameError使用了未定义的变量
自定义异常
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 class MyError (Exception ):def __init__ (self, message ):def __str__ (self ):return self.messagetry :raise MyError("MyError" )except MyError as e:print (e)
文件 打开文件
1 f = open (file, mode='r' , encoding=None )
打开模式
模式
含义
文件不存在时行为
可读
可写
是否清空原文件
r只读
❌ 报错
✅
❌
否
w只写
✅ 创建新文件
❌
✅
✅ 清空
a追加写入
✅ 创建新文件
❌
✅
❌(在末尾写)
r+读写
❌ 报错
✅
✅
❌
w+写读(先清空)
✅ 创建新文件
✅
✅
✅ 清空
a+读写(追加写入)
✅ 创建新文件
✅
✅
❌(只追加)
rb/wb 等二进制读写
适合图片、音频等
看上面
看上面
看上面
写入文件
使用with open() as f会自动关闭文件,不然要手动f.close()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 with open ("test.txt" , "w" , encoding="utf-8" ) as f:"Hello, world!\n" )"Second line.\n" )with open ("test.txt" , "a" , encoding="utf-8" ) as f:"Appended line.\n" )
读取文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 with open ("test.txt" , "r" , encoding="utf-8" ) as f:print (content)with open ("test.txt" , "r" , encoding="utf-8" ) as f:for line in lines:print (line.strip())
迭代器 访问集合元素的一种方式
可以记住遍历的位置的对象,只能往前不会后退
使用 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 1 , 2 , 3 ]iter (a)print (next (b)) print (next (b)) print (next (b)) print (next (b)) for i in iter (a):print (i)
创建迭代器 实现__iter__()和__next__()方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class MyNum :def __iter__ (self ):0 return selfdef __next__ (self ):if tmp < 20 :1 return tmpelse :raise StopIteration iter (myclass)for i in it:print (i)
生成器 使用了yield的函数 被称为生成器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 def countdown (n ):while n > 0 :yield n1 5 )print (next (generator)) print (next (generator)) print (next (generator)) for value in generator:print (value)
函数 不定长参数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 def method (var1, *var2 ):print (var1, " " ,var2)1 ) 1 , 2 ) 1 , 2 , 3 )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 def method (var1, *var2, **var3 ):print (var1)print (var2)print (var3)1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 , a = 1 , b = 2 )''' 1 (2, 3, 4, 5) {'a': 1, 'b': 2} '''
匿名函数
作用是为了简洁,性能上和普通函数没差
1 2 3 4 5 sum = lambda arg1, arg2: arg1 + arg2print ("相加后的值为 : " , sum (10 , 20 )) print ("相加后的值为 : " , sum (20 , 20 ))
函数装饰器 函数装饰器是一种函数,它接受一个函数作为参数,并返回一个新的函数或修改原来的函数
用于不修改原函数的基础上动态地增加或修改函数的功能
类似java的注解+AOP
基本语法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 def decorator_function (original_function ):def wrapper (*args, **kwargs ):return resultreturn wrapper@decorator_function def target_function (arg1, arg2 ):pass
实例 :函数执行时间
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 import timedef time_logger (func ):def wrapper (*args, **kwargs ):print ("参数: " , args)print ("执行时间: " , end_time - start_time)return resreturn wrapper@time_logger def say_hello (name ):print ("Hello! " , name)0.5 )"Alice" )
实例 :带参数的装饰器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 def repeat (n ):def decorator (func ):def wrapper (*args, **kwargs ):for i in range (n):return wrapperreturn decorator@repeat(3 def say_hello ():print ("Hello World!" )
类装饰器 类装饰器用于动态修改类行为
实例 :实现类的单例
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class SingletonDecorator :"""类装饰器,使目标类变成单例模式""" def __init__ (self, cls ):None def __call__ (self, *args, **kwargs ):"""拦截实例化过程,确保只创建一个实例""" if self.instance is None :return self.instance@SingletonDecorator class Database :def __init__ (self ):print ("Database 初始化" )print (db1 is db2)
面向对象 构造方法 __init()__,创建对象时自动调用
不写默认是个空的构造方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 class Person :def __init__ (self, name, age ):"John" , 22 )print (p.age)print (p.name)
类方法 类方法用def定义,且第一个参数要为self
继承 子类继承父类的属性和方法
子类里可用super().来调用父类的方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Animal :def speak (self ):print ("动物在叫" )class Dog (Animal ):def bark (self ):print ("汪汪汪" )
多继承 时决定调用哪个类的方法,按从左到右的优先级
即先找自己,在从左到右找父类(如果父类也有父类,则会顺着它的父类找上去)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class A :def hello (self ):print ("A" )class B (A ):def hello (self ):print ("B" )class C (A ):def hello (self ):print ("C" )class D (B, C):pass
私有属性和方法 定义:在属性或方法前加__
私有属性和方法只能在本类中访问
python的私有并不是真的私有,只是改了其名字,变为_类型__属性名
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Person :def __init__ (self, name, age ):def __say_secret (self ): print ("这是一个秘密" )def show (self ):print (f"{self.__name} , {self.__age} " )print (Person("Tom" , 20 ).show())
魔法方法 魔法方法是 Python 自动调用的一些特殊方法
方法
作用
__init__(self, ...)构造函数,创建对象时调用
__new__(cls, ...)真正创建对象的方法,__init__ 前执行(用于元类)
__del__(self)析构函数,删除对象时调用
__str__()print(obj) 时调用
__repr__()解释器或 repr(obj) 时调用
运算符重载
方法
对应操作
__add__+ 加法
__sub__- 减法
__mul__* 乘法
__eq__== 比较
__lt__< 小于
多线程 Python的多线程是并发 的,而非真正的并行
CPython使用全局解释器锁(GIL)来保证线程安全,即同一时刻只有一个线程可以执行Python字节码。即使有多核CPU,GIL也会阻止多线程的并行 执行
通过threading模块来使用多线程
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 import threadingimport timedef say_hello ():for i in range (3 ):print (f"线程 {threading.current_thread().name} 打招呼" )1 )'T1' )'T2' )print ("主线程结束" )
功能
说明
Thread(target=...)创建线程并指定要执行的函数
start()启动线程
join()阻塞,直到被调用线程终止
current_thread()获取当前线程信息
Lock()创建互斥锁,防止多线程同时修改共享数据
enumerate()返回一个包含正在运行的线程的列表
active_count()返回正在运行的线程数量
守护线程
主线程会等待普通线程结束后才结束,而不会等待守护线程
要在start()前设置t.daemon = True才为守护线程
适合做后台服务或辅助任务
线程同步 互斥锁
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 import threading0 def add ():global countfor _ in range (100000 ):with lock:1 print ("count:" , count)
可重入锁
threading.RLock()
支持一个线程加多次锁,适合递归或多个函数都加锁时
信号量
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 import threadingimport time3 ) def task ():with sem:print (threading.current_thread().name, "进入" )2 )
线程通知
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 import threadingimport timedef worker ():print ("等待事件触发..." )print ("事件已触发,开始工作" )3 )print ("触发事件!" )set ()
JSON 通过dump()转换为json格式,load()读取json
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 import json'name' : 'Bob' , 'age' : 30 , 'is_student' : True }with open ('data.json' , 'w' ) as f:4 , ensure_ascii=False )with open ('data.json' , 'r' ) as f:print (data)
Numpy
NumPy 是一个用于处理数组的 Python 库,主要用于矩阵运算
数组属性
Numpy的数组类被称为ndarray
维度 :ndarray.ndim形状 :ndarray.shape数组包含元素的数量 :ndarray.size元素类型 :ndarray.dtype元素的大小 :ndarray.itemsize
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 import numpy as np15 ).reshape(3 , 5 )print ("数组的形状: " , a.shape)print ("数组的维数: " , a.ndim)print ("数组元素类型: " , a.dtype)print ("数组中每个元素的字节大小" , a.itemsize)print ("数组元素的总个数: " , a.size)print ("类型查询: " , type (a))
创建数组 整数数组 1 2 3 4 5 import numpy as np1 , 2 , 3 ])print (ar1)
浮点型数组 1 2 3 1.0 , 2 , 3 ])print (ar2)
全为1或0的数组 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 3 , 3 )) print (arr1)print (arr1.shape) print (arr1.reshape((1 , -1 ))) print (arr1.reshape(-1 ))
递增数组 1 2 3 1 , 10 , 2 , dtype=int )print (arr1)
随机数组 1 2 3 4 5 6 3 , 5 ) 1 , 10 , size=(3 , 5 )) 1 , 10 , size=(3 , 5 )) 0 , 1 , size=(3 , 5 )) print (arr1)
等比数组 1 2 3 4 5 0 , 3 , 5 , endpoint=True , base=10 )print (arr1)
等差数列 1 2 3 0 , 10 , 5 )print (arr1)
转换类型 1 2 3 4 arr1 = np.arange(15 ).reshape(3 , 5 )print (arr1.dtype) print (arr2.dtype)
内置函数
基本函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 arr1 = np.random.randn(3 , 4 )print (arr1)print (np.sum (arr1)) print (np.ceil(arr1)) print (np.floor(arr1)) print (np.rint(arr1)) print (np.abs (arr1)) print (np.multiply(arr1, arr1)) print (np.divide(arr1, arr1)) print (np.where(arr1 > 0 , 1 , -1 ))
统计函数
1 2 3 4 5 arr1 = np.arange(12 ).reshape(3 , 4 )print (arr1)print (np.cumsum(arr1)) print (np.sum (arr1, axis=0 )) print (np.sum (arr1, axis=1 ))
去重函数
1 2 arr1 = np.array([[1 , 2 , 1 ], [3 , 4 , 5 ]])print (np.unique(arr1))
排序函数
1 2 arr1 = np.array([[1 , 2 , 1 ], [3 , 4 , 5 ]])print (np.sort(arr1))
访问数组 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 arr1 = np.array( [[1 , 2 , 3 ], [4 , 5 , 6 ]])print (arr1[0 , 1 ])print (arr1[ [0 , 1 ], [1 , 2 ] ])
数组操作 切片
numpy的切片仅是原数组的视图,原python的是拷贝。要拷贝用数组.copy()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1 , 21 ).reshape(4 , 5 )print (arr1)print (arr1[1 :3 , 1 :-1 ])
翻转 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 import numpy as np10 )print (arr1) 1 , 21 ).reshape(4 , 5 )print (arr1)print (arr1)
转置 重塑 1 2 3 , 4 ))
拼接 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1 , 2 , 3 ])4 , 5 , 6 ])print (np.concatenate((arr1, arr2))) 1 , 2 , 3 ], [4 , 5 , 6 ]])7 , 8 , 9 ]])print (np.concatenate((arr1, arr2)))
截断 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 ])print (np.split(arr1, (2 , 4 ))) 8 ).reshape(2 , -1 )print (np.split(arr1, (1 , ), axis=1 ))
矩阵运算 相乘 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 5 )5 )print (np.dot(arr1, arr2))5 )15 ).reshape(5 , 3 )print (np.dot(arr1, arr2))
数学函数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 10 , 0 , 10 ))print (np.abs (arr1))print ("2^x = " , 2 ** arr1)print ("log2(x) = " , np.log(arr1) / np.log(2 ))2 , 4 , 6 ), (1 , 2 , 3 )))print (np.max (arr1, axis=0 ))
布尔 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 False , False , True ))print (np.any (arr1)) print (np.all (arr1)) 1 , 2 , 3 ))print (arr1[ arr1 > 1 ]) 1 , 2 , 3 ))print (np.where(arr1 > 1 ))
Pandas
Pandas 提供了易于使用的数据结构和数据分析工具,特别适用于处理结构化数据,如表格型数据。可以看做是numpy的扩展
创建数据结构 Series
包含一行或一列数据
可通过列表、元组、字典、numpy数组来创建
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 import pandas as pd'a' : 0 , 'b' : 0.25 , 'c' : 0.75 , 'd' : 1 }print (sr)'a' , 'b' , 'c' , 'd' ]0 , 0.25 , 0.75 , 1 ]print (sr)
DataFrame
一个 DataFrame 可以看作是由多个 Series 按列组合而成
类似二维表格
通过字典创建
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 data = {'name' : ['A' , 'B' , 'C' , 'D' , 'E' ],'gender' : ['male' , 'female' , 'male' , 'female' , 'male' ],'age' : [1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ]print (df1)
通过数组创建
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 info = ['A' , '女' , 20 ),'B' , '男' , 21 ),'C' , '男' , 22 ),'name' , 'gender' , 'age' ])print (df2)
通过numpy的ndarray创建
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 arr1 = np.arange(12 ).reshape(3 , 4 )'A' , 'B' , 'C' , 'D' ])print (df3)
访问 Series
如果key是数字的话,会和下标混淆,所有可以用loc显示索引(key),iloc隐式索引(下标)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 k = ['a' , 'b' , 'c' , 'd' ]0 , 0.25 , 0.75 , 1 ]print (sr['c' ])print (sr.loc['c' ])print (sr['a' :'c' ])print (sr[0 :2 ])
DataFrame 必须使用索引器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 v = np.array([ [53 , '女' ], [64 , '男' ], [72 , '女' ], [82 , '男' ] ])'1号' , '2号' , '3号' , '4号' ]'年龄' , '性别' ]print (df.iloc[0 ][0 ])print (df.loc['1号' ]['年龄' ])print (df.loc['1号' :'3号' , '年龄' ])
基本函数 DataFrame
功能分类
函数 / 属性名称
作用描述
数据查看与信息 head(n)查看前 n 行数据(默认 5 行),快速预览数据结构
tail(n)查看后 n 行数据(默认 5 行)
shape返回元组 (行数, 列数),获取数据维度
info()输出列名、数据类型、非空值数量、内存占用等基本信息
describe()对数值列进行统计描述(均值、标准差、最值等),非数值列默认不显示
columns返回列名列表,查看所有列的名称
index返回行索引(标签),查看所有行的标识
数据选择与筛选 loc[]通过行 / 列标签(名称) 选择数据,支持切片和条件筛选
iloc[]通过行 / 列位置索引(整数) 选择数据,类似列表切片
[](方括号)简化选择:传入列名选列(如 df['col']),或布尔数组筛选行
filter()按规则筛选列(支持正则、包含关系等,如 df.filter(like='key'))
数据修改与处理 drop()删除指定行 / 列(需指定 axis,如 axis=1 删列)
rename()修改列名或行索引(通过 columns 或 index 参数)
fillna()填充缺失值(如 df.fillna(0) 用 0 填充,或 method='ffill' 向前填充)
dropna()删除包含缺失值的行 / 列(默认删行,axis=1 删列)
replace()替换数据中的特定值(如 df.replace(0, -1) 将 0 替换为 -1)
astype()转换列的数据类型(如 df['col'].astype('int') 转为整数型)
数据运算与统计 sum()计算列 / 行的求和(默认列求和,axis=1 行求和)
mean()计算平均值
max()/min()计算最大值 / 最小值
value_counts()统计某列中各值的出现次数(通常用于离散型数据)
groupby()按指定列分组,用于分组统计(如 df.groupby('category')['value'].mean())
数据合并与连接 merge()类似 SQL 连接,按指定列合并两个 DataFrame(支持内连接、外连接等)
concat()沿指定轴(行 / 列)拼接多个 DataFrame(如 pd.concat([df1, df2]))
append()在末尾追加行(已逐渐被 concat 替代)
其他常用操作 sort_values()按指定列排序(by 参数指定列,ascending 控制升序 / 降序)
pivot_table()创建透视表,用于数据聚合分析
to_csv()将 DataFrame 保存为 CSV 文件
read_csv()从 CSV 文件读取数据并生成 DataFrame(pandas 模块函数,非 DataFrame 方法)
例子
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 import pandas as pd'./data/stock_day.csv' )print (df.head())'ma5' , 'ma10' , 'ma20' , 'v_ma5' , 'v_ma10' , 'v_ma20' ], inplace=True )print (df['open' ]['2015-03-06' ]) print (df.loc['2018-02-27' :'2018-02-14' , 'open' ]) print (df.iloc[0 :5 , 0 ]) '2018-02-27' , 'open' ] = 23 'open' , ascending=False ) print (df.head())print (df['close' ] + 2 )print (df[df['open' ] > 23 ]) print (df.query('open > 23 and open < 24' )) print (df.query('open == 23.53 or open == 23.67' )) print (df[df['open' ].isin([23.53 , 23.67 ])])
对象变形
转置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 v = [[53 , 64 , 72 , 82 ], ['女' , '男' , '女' , '男' ]]'年龄' , '性别' ]'1号' , '2号' , '3号' , '4号' ]print (df.T)
翻转
1 2 3 4 print (df.T.iloc[: : -1 , :])print (df.T.iloc[:, : : -1 ])
重塑
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 i = ['1号' , '2号' , '3号' , '4号' ]10 , 20 , 30 , 40 ]'女' , '男' , '女' , '男' ]1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ]'年龄' : sr1, '性别' : sr2})'拍照' ] = sr3print (df)
合并
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 0 )1 )'inner' , on=['key1' , 'key2' ])
分组
分组查询
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 import pandas as pd"./data/uniqlo.csv" )'city' , 'channel' ])print (group1.get_group(('北京' , '线下' )))print (group1.agg({'revenue' : 'sum' }))
分组过滤
1 group1 = df.groupby(['city' ]).filter (lambda x: x['revenue' ].mean() > 200 )
缺失值处理 找缺失值
Series
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 import pandas as pd1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ]1 , 2 , 3 , None ]print (sr.isnull())
DataFrame
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 v = [ [None , 1 ], [64 , None ], [72 , 3 ], [82 , 1 ]]'1号' , '2号' , '3号' , '4号' ]'年龄' , '牌照' ]print (df.isnull())
剔除缺失值
填充缺失值
Series
1 2 3 4 5 k = [1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ]1 , 2 , 3 , None ]print (sr.fillna(0 ))
DataFrame
1 2 3 4 5 6 v = [ [None , 1 ], [64 , None ], [72 , 3 ], [82 , 1 ]]'1号' , '2号' , '3号' , '4号' ]'年龄' , '牌照' ]print (df.fillna(0 ))
读取文件 CSV 导入/导出
增删改查
增
1 2 3 4 5 df = pd.read_csv('./data/1960-2019全球GDP数据.csv' , encoding='gbk' )5 ].copy()'c1' ] = 10 'c2' ] = ['A' , 'B' , 'C' , 'D' , 'E' ]
删
删除行
1 2 0 , 2 , 4 ], inplace=True )
删除列
1 2 3 4 del df2['year' ]'country' ], inplace=True )
去重
1 2 3 4 True )
改
新增一列
修改
1 2 3 4 'GDP' ] = [1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ]'country' ].replace('美国' , 'usa' )
查
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 df.head(n) 'year' ] 'year' ]] 5 ] 1 :5 :2 ] 10 ::5 ] False ) 'year' , ascending=False )
MySQL
需要安装包
pip install pymysql
pip install sqlalchemy
读写
写入数据
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 from sqlalchemy import create_engineimport pandas as pd'mysql+pymysql://root:123456@127.0.0.1:3306/test?charset=utf8' )'./data/csv示例文件.csv' , encoding='gbk' , index_col=0 )'my_table' , con=engine, if_exists='append' , index=False )
读取数据
1 2 3 4 'my_table' , con=engine)'select name from my_table' , con=engine)
Json 导入/导出
导入json数据
1 2 3 4 5 6 './data/test.json' , orient='records' , lines=True )
导出为json文件
1 json_df.to_json('./data/my_file3.json' , orient='records' )
Matplotlib 绘图基础 绘制图像 绘制一条线
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ] 1 , 8 , 27 , 64 , 125 ]
绘制多条线
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ]1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ]0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 ]1 , -2 , -3 , -4 , -5 ]
绘制多子图
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ]1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ]0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 ]1 , -2 , -3 , -4 , -5 ]3 , 1 , 1 ) 3 , 1 , 2 )3 , 1 , 3 )
保存图像 图标类型 要画什么类型的图时去官网找样例改
https://matplotlib.org/stable/plot_types/index
二维图
只需要两个向量
类型
方法
线型图
plot()
散点图
scatter()
条形图
bar()
杆图
stem()
阶梯图
step()
误差图
fill_between()
堆叠图
stackplot()
网格图
需要一个矩阵
类型
方法
图像展示
imshow()
等高线
contour()
填充等高线
contourf()
统计图
需要一个矩阵
类型
方法
直方图
hist()
箱型图
boxplot()
二维直方图
hist2d()
饼图
pie()
PyTorch
DNN:Deep Neural Network,深度神经网络
张量
张量是一个 数学对象 ,可以看作是 坐标系无关的多维数据结构 ,它能在不同坐标系下转换但仍然保持物理意义。可以把张量理解为多维数组
用GPU存储张量 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 import torch3 , 4 )print (ts1)'cuda:0' )print (ts2)
DNN大致原理 神经网络通过学习大量样本的输入与输出特征之间的关系,以拟合出输入与输出之间的方程。
神经网络可以分为这几步:
划分数据集
按一定比例划分为训练集和测试集。数据集的特征决定了输入层和输出层的神经元
训练网络
通过多次的前向传播和反向传播,不断调整内部参数,以拟合任意复杂函数的过程
内部参数称为参数,外部参数称为超参数
前向传播:
将输入特征通过神经网络逐层计算,最终得到输出特征
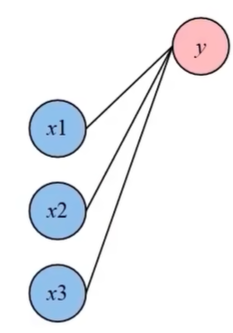
神经元节点的计算过程:
y = w1 x1 + w2 x2 + w3 x3
由于方程是线性的,因此必须在外面套一个非线性的函数σ,称为激活函数
反向传播:
经过前向传播得到预测值后,通过损失函数计算差距,通过调整参数使得损失函数变小
测试网络
使用测试集正向传播来测试准确率
使用网络
DNN的实现 查看损失函数、激活函数、层、优化算法等的文档,记得选择自己的版本:http://pytorch.org/docs/1.12/nn.html
批量梯度下降
一次性用 整个训练集 计算梯度,再更新权重
优点:
缺点:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 import torchimport torch.nn as nnimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltclass DNN (nn.Module):def __init__ (self ):""" 搭建神经网络各层 """ super (DNN, self).__init__()3 , 5 , ), nn.ReLU(), 5 , 5 , ), nn.ReLU(), 5 , 5 , ), nn.ReLU(), 5 , 3 , ), nn.ReLU() def forward (self, x ):""" 前向传播 """ """ 张量会自动计算梯度,不需要反向传播方法 """ return y 10000 , 1 )10000 , 1 )10000 , 1 )1 ).float ()1 ) & ((X1 + X2 + X3) < 2 ) ).float ()2 ).float ()1 )'cuda:0' )int (len (Data) * 0.7 )len (Data) - train_size0 )), :] 'cuda:0' )0.01 1000 3 ]3 :]for epoch in range (epochs):range (epochs), losses)'epoch' )'loss' )3 ]3 :]with torch.no_grad(): 1 )] = 1 1 ] = 0 sum ( (Pred == Y).all (1 ) )0 )print (f'测试集精准度: {100 * correct / total} %' )
保存/导出神经网络
1 torch.save(model, 'model.pth' )
导入神经网络
1 new_model = torch.load('model.pth' )
从csv文件里导入数据
1 2 3 4 5 6 'Data.csv' , index_col=0 ) 'cuda' )
小批量梯度下降
把训练集划分成若干 小批量(mini-batch) ,每次只用一个批量计算梯度再更新。
优点:
计算效率高,比批量梯度下降快
梯度有随机性,能跳出局部最优
适合 GPU 并行计算
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 import numpy as npimport pandas as pdimport torchfrom torch.utils.data import Dataset, random_split, DataLoaderimport torch.nn as nnimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltclass DNN (nn.Module):def __init__ (self ):""" 搭建神经网络各层 """ super (DNN, self).__init__()8 , 32 , ), nn.Sigmoid(), 32 , 8 , ), nn.Sigmoid(), 8 , 4 , ), nn.Sigmoid(), 4 , 1 , ), nn.Sigmoid() def forward (self, x ):""" 前向传播 """ """ 张量会自动计算梯度,不需要反向传播方法 """ return y 'cuda' )class MyData (Dataset ):def __init__ (self, filepath ):0 ) 'cuda' )1 ]1 ].reshape((-1 , 1 ))len = ts.shape[0 ]def __getitem__ (self, index ):return self.X[index], self.Y[index]def __len__ (self ):return self.len 'Data.csv' )int (0.7 * len (Data))len (Data) - train_size128 , shuffle=True )64 , shuffle=False )500 'mean' )0.005 for epoch in range (epochs):for (x, y) in train_loader:range (len (losses)), losses)
MNIST数据集
一个0-9数字识别的数据集
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 import torchfrom torch.utils.data import Dataset, random_split, DataLoaderimport torch.nn as nnimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom torchvision import transforms from torchvision import datasets 0.1307 , 0.3081 )'./dataset/mnist/' ,True ,True './dataset/mnist/' ,False ,True class DNN (nn.Module):def __init__ (self ):""" 搭建神经网络各层 """ super (DNN, self).__init__()784 , 512 , ), nn.ReLU(),512 , 256 , ), nn.ReLU(),256 , 128 , ), nn.ReLU(),128 , 64 , ), nn.ReLU(),64 , 10 , ), nn.ReLU(),def forward (self, x ):""" 前向传播 """ """ 张量会自动计算梯度,不需要反向传播方法 """ return y 'cuda:0' )64 , shuffle=True )64 , shuffle=False )0.01 0.5 5 for epoch in range (epochs):for (x, y) in train_loader:'cuda:0' ), y.to('cuda:0' )range (len (losses)), losses)
CNN和DNN的区别
CNN: Convolutional Neural Network,卷积神经网络
特性
DNN(深度神经网络)
CNN(卷积神经网络)
基本单元 全连接层(每个神经元都与前一层所有神经元相连)
卷积层 + 池化层
参数量 参数多(因为全连接)
参数少(卷积核共享权重)
特征提取 人工设计特征,输入通常是向量
自动提取局部特征,适合图像/时序
输入格式 一维向量
二维/三维张量(图像:高×宽×通道)
适用场景 简单分类、回归、推荐系统
图像识别、目标检测、语音识别、NLP(部分场景)
CNN的大致原理 内部参数:卷积核
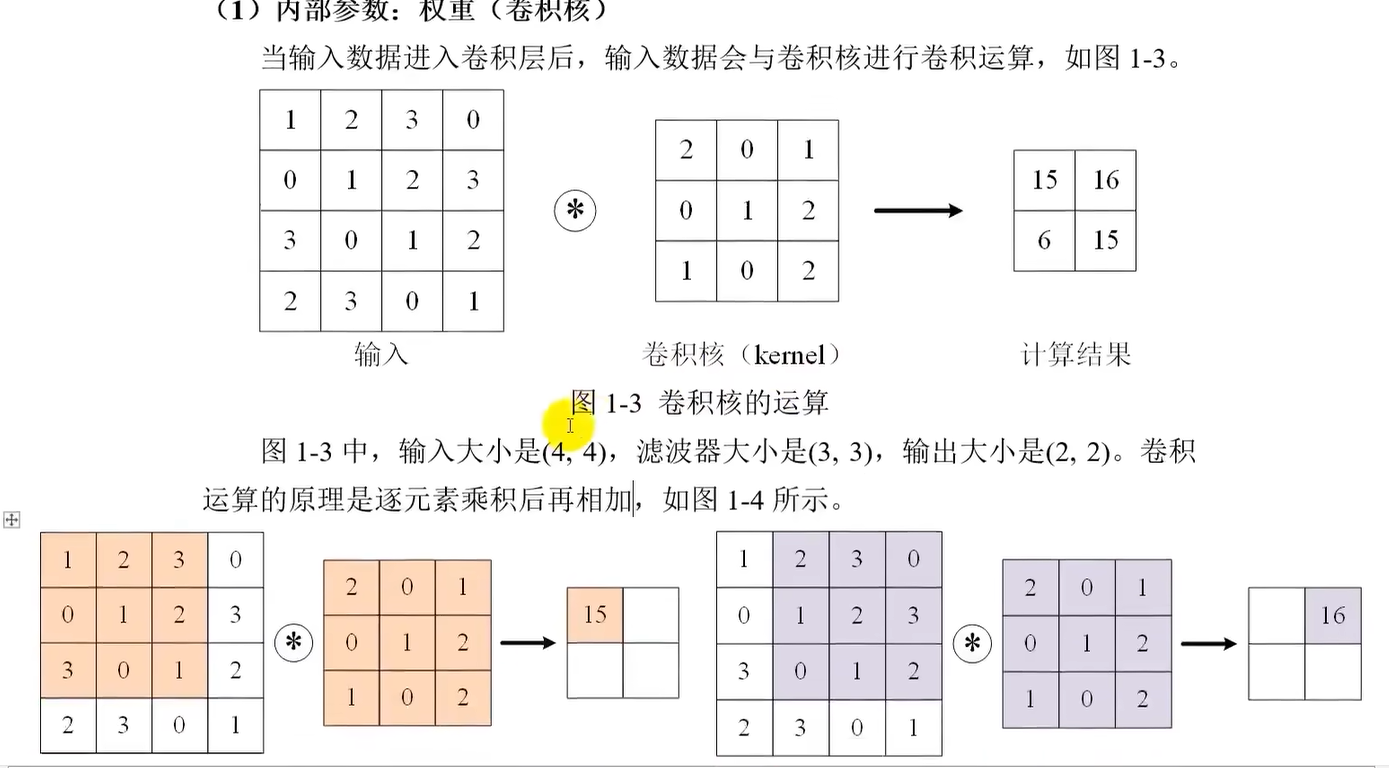
当输入数据进入卷积层后,会与卷积核(类似DNN的权重)进行卷积运算
当输入数据是二维时被称为卷积核,三维及以上时称为滤波器
内部参数:偏置
将卷积运算结果加上偏置的值
外部参数:填充
为了防止经过多个卷积层后图像越来越小,向图像的周围填充固定的数据(如0)
外部参数:步幅
使用卷积核的位置,每次往右移动1格就是步幅为1
输入和输出尺寸的关系
可通过调节步幅和尺寸来控制某层输出尺寸
多通道输出
让三维的特征多经过几个卷积层,每层都有单独的偏置
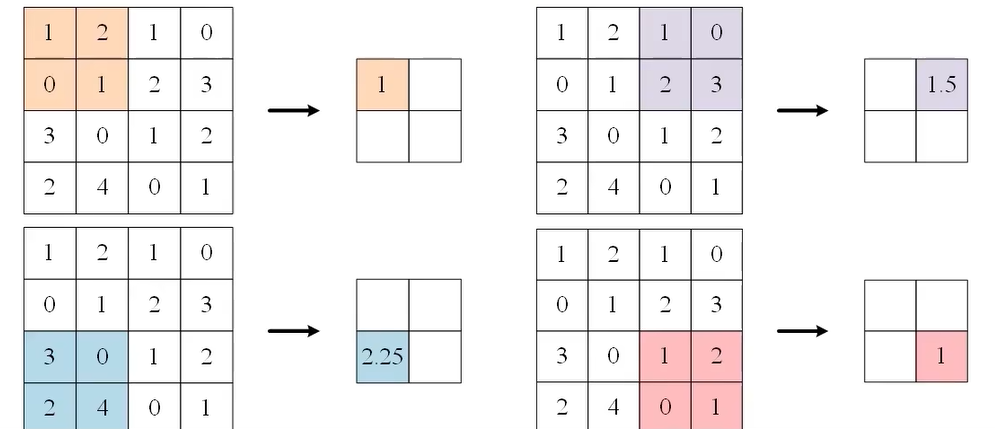
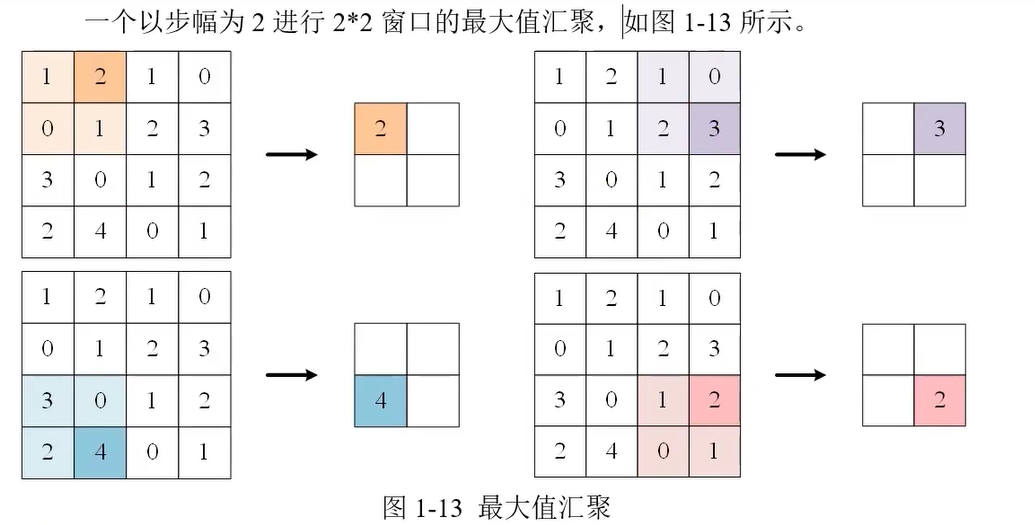
汇聚(池化)
从一个范围内提取一个特征值,不会改变通道数
平均汇聚
最大值汇聚
尺寸变换总结
汇聚只要高和宽除以步长就行
CNN模型 LeNet-5
LeNet-5 是卷积神经网络(CNN)发展史上的一个里程碑模型,1998 年提出,第一个真正成功应用在图像识别上的 CNN 架构,为后来的 AlexNet、VGG、ResNet 奠定了基础
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 import torchfrom torch.utils.data import Dataset, random_split, DataLoaderimport torch.nn as nnimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom torchvision import transforms from torchvision import datasets 0.1307 , 0.3081 )'./dataset/mnist/' ,True ,True './dataset/mnist/' ,False ,True 256 , shuffle=True )256 , shuffle=False )class CNN (nn.Module):def __init__ (self ):super ().__init__()1 , 6 , kernel_size=5 , padding=2 ), nn.Tanh(), 2 , stride=2 ), 6 , 16 , kernel_size=5 ), nn.Tanh(), 2 , stride=2 ), nn.Tanh(), 16 , 120 , kernel_size=5 ), nn.Tanh(), 120 , 84 ), nn.Tanh(), 84 , 10 ) def forward (self, x ):return self.net(x)'cuda:0' )0.9 5 for epoch in range (epochs):for (x, y) in train_loader:'cuda:0' ), y.to('cuda:0' )range (len (loss_list)), loss_list)0 0 with torch.no_grad():for x, y in test_loader:'cuda:0' ), y.to('cuda:0' )max (Pred.data, 1 )sum ((predicted == y))0 )print (f'精度:{100 * correct / total} %' )
AlexNet
AlexNet 是一个经典的 卷积神经网络(CNN)结构 ,由 Alex Krizhevsky 在 2012 年提出,用于图像分类。它在 ImageNet 图像识别竞赛 (ILSVRC 2012)上夺冠,把前一年的错误率从 26% 一下子降到 15% 左右 ,震惊了整个计算机视觉领域,也标志着 深度学习在视觉任务上的崛起 。
GoogLeNet
最特别的地方是 Inception 模块 (也叫“Google Inception”),怎么在同一层里兼顾不同大小的卷积核 的问题。
ResNet
ResNet,全称 Residual Network(残差网络) ,是 微软研究院 在 2015 年提出的 CNN 架构。ImageNet 2015 比赛里直接拿了冠军,把网络层数推到了 152 层 ,但依然能很好训练,性能远超前辈。
是一种解决深层网络退化问题的 CNN,通过“残差连接”让信息和梯度能顺畅流动,从而能训练几十甚至上百层的网络。