Netty
Netty是 一个异步事件驱动的网络应用程序框架,用于快速开发可维护的高性能协议服务器和客户端。
NIO基础
NIO(non-blocking io)非阻塞IO
三大组件
Channel
读写数据的双向通道
常见Channel有:
- FileChannel:传输文件
- DatagramChannel:UDP
- SocketChannel:TCP
- ServerSocketChannel:TPC,专用于服务器
Buffer
缓冲读写数据
常见Buffer有:
Selector
在服务器和用户连接上的几种策略:
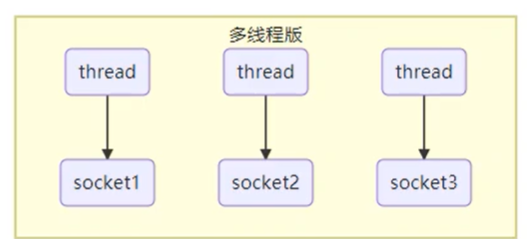
- 多线程:一个线程对应一个用户(socket)。缺点:内存占用高,上下文切换成本高,只适合连接少的场景
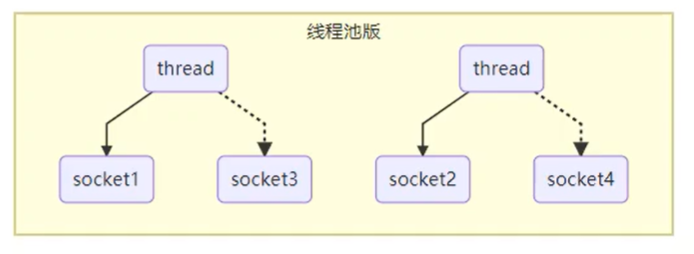
- 线程池:一个线程池对应多个用户(socket)。缺点:阻塞模式下,线程仅能处理一个socket,仅适合短连接场景
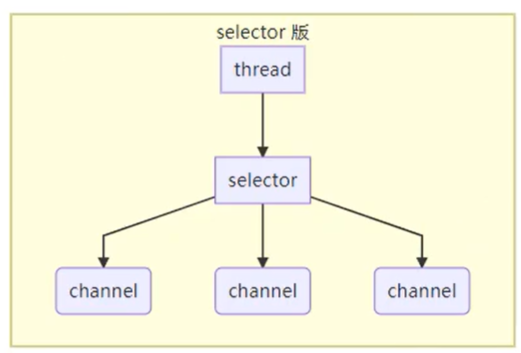
- selector:一个selector和一个线程管理多个channel,当channel有任务要线程处理时,由selector通知线程去处理,线程是非阻塞的。适合连接多,流量低的场景。
ByteBuffer
基本使用
功能:在项目目录下创建一个data.txt文件,读取这个文件的内容
使用步骤:
- 像buffer写入数据,如channel.read(buffer)
- 调用filp()切换至读模式
- 从buffer中读取数据,如buffer.get()
- 调用clear()或compact()切换至写模式
- 重复以上步骤
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (FileChannel channel = new FileInputStream("data.txt").getChannel()){
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
while (channel.read(buffer) != -1) {
buffer.flip();
while (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
System.out.println((char) buffer.get());
}
buffer.clear();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
|
结构
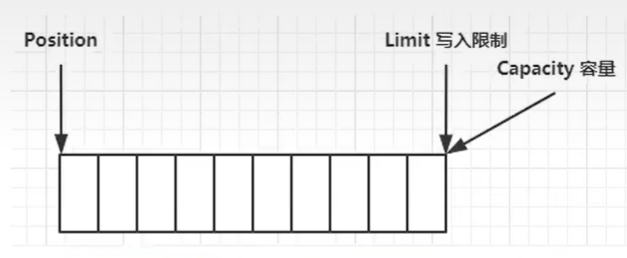
属性:
- capacity 容量
- position 读写指针
- limit 读写的尾部指针
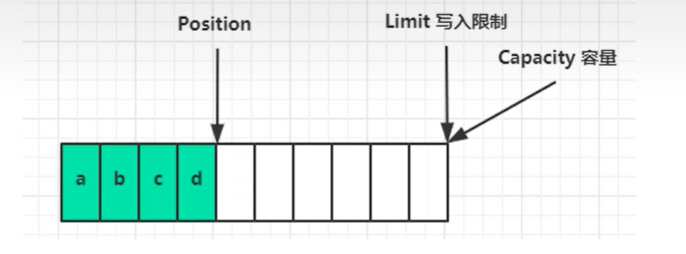
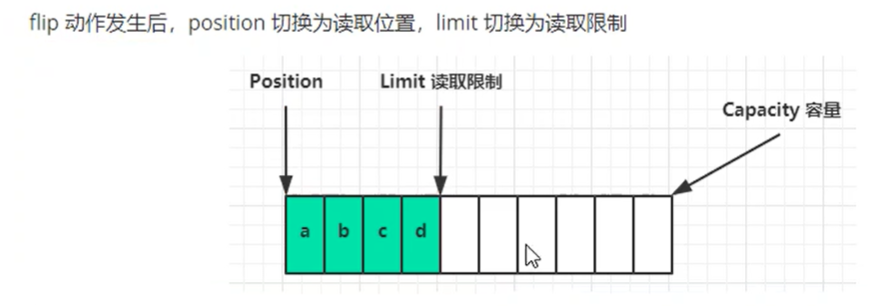

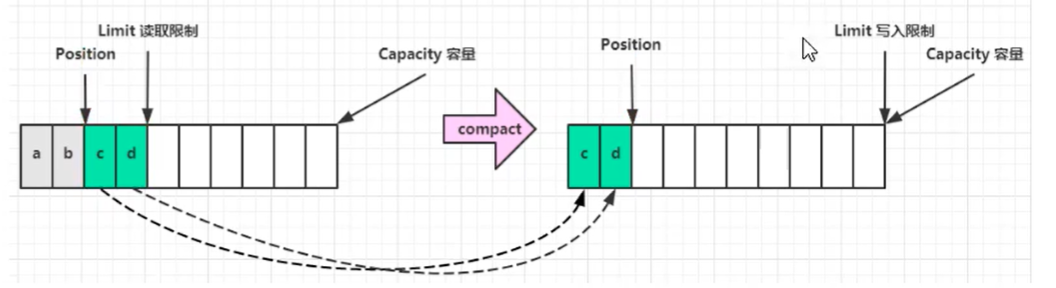
常见方法
分配空间
分配一块固定的容量(字节)
1
2
3
4
5
|
ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(16);
|
写入数据
1
2
3
4
|
channel.read(buffer);
buffer.put();
|
读取数据
1
2
3
4
|
channel.write(buffer);
buffer.get();
|
- rewind() 将position移到头部
- get(int idx) 读取指定下标的数据,不会改变position指针
做标记
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
buffer.put(new byte[]{'a', 'b', 'c', 'd'});
buffer.flip();
System.out.println(buffer.get());
buffer.mark();
System.out.println(buffer.get());
System.out.println(buffer.get());
buffer.reset();
System.out.println(buffer.get());
|
String和ByteBuffer转换
1
2
3
4
|
ByteBuffer buffer1 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("hello");
System.out.println(StandardCharsets.UTF_8.decode(buffer1).toString());
|
粘包、半包
粘包:
- 传输换行的数据时,多行数据在一行传输
- 是在效率上考虑,多条一起发效率高
半包:
- 一行数据被拆成多行显示
- 因为缓冲区大小导致数据被拆
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteBuffer source = ByteBuffer.allocate(32);
source.put("Hello,world\nI'm zhangsan\nHo".getBytes());
split(source);
source.put("w are you?\n".getBytes());
split(source);
}
private static void split(ByteBuffer source) {
source.flip();
for (int i = 0; i < source.limit(); i++) {
if (source.get(i) == '\n') {
int length = i - source.position() + 1;
ByteBuffer target = ByteBuffer.allocate(length);
for (int j = 0; j < length; j++) {
target.put(source.get());
}
target.flip();
System.out.println(StandardCharsets.US_ASCII.decode(target));
}
}
source.compact();
}
|
文件编程
FileChannel
FileChannel只能工作在阻塞模式下,不能使用selector
获取方式
- FileInputStream:获取的channel只能读
- FileOutputStream:获取的channel只能写
- RandomAccessFile:根据构造RandomAccessFile时的读写模式决定
读取
1
| int readBytes = channel.read(buffer);
|
写入
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| ByteBuffer buffer = ...;
buffer.put(...);
buffer.flip();
while (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
channel.write(buffer);
}
|
关闭
强制写入
为了减少io操作,写的数据不会立即写到磁盘中。可以调动force(true)立即写入磁盘
传输数据到另一个文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| try (
FileChannel from = new FileInputStream("data.txt").getChannel();
FileChannel to = new FileOutputStream("to.txt").getChannel();
) {
long size = from.size();
for (long left = size; left > 0;)
left -= from.transferTo(size - left, left, to);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
|
Path & Files
Path用于表示文件路径
Paths是工具类,用于获取Path实例
1
| Path source = Paths.get("1.txt");
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
Path path = Path.get("data.txt");
System.out.println(Files.exists(path));
Path path = Path.get("hello/d1");
Files.createDirectory(path);
Path path = Path.get("hello/d1/d2");
Files.createDirectorys(path);
Path source = Path.get("helloword/data.txt");
Path target = Path.get("helloword/target.txt");
Files.copy(source, target);
Files.walkFileTree(Paths.get("F:\\aaa"), new SimpleFileVisitor<Path>(){
@Override
public FileVisitResult preVisitDirectory(Path dir, BasicFileAttributes attrs) throws IOException {
System.out.println(dir);
return super.preVisitDirectory(dir, attrs);
}
@Override
public FileVisitResult visitFile(Path file, BasicFileAttributes attrs) throws IOException {
System.out.println(file);
return super.visitFile(file, attrs);
}
});
。。。
|
:star:网络编程
阻塞&非阻塞
单线程模式下
阻塞模式
单线程不能很好的处理多个连接
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
ssc.bind(new InetSocketAddress((8080)));
List<SocketChannel> socketChannels = new ArrayList<>();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);
while (true) {
SocketChannel sc = ssc.accept();
socketChannels.add(sc);
for (SocketChannel channel : socketChannels) {
channel.read(buffer);
buffer.flip();
while (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
System.out.print((char) buffer.get());
}
System.out.println();
buffer.clear();
}
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
SocketChannel sc = SocketChannel.open();
sc.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080));
sc.write(StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("asd"));
}
}
|
非阻塞模式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
ssc.configureBlocking(false);
SocketChannel sc = ssc.accept();
sc.configureBlocking(false);
channel.read(buffer);
|
Selector
多路复用:单线程配合Selector完成对多个Channel可读写事件的监控
事件的种类
- accept:服务端在有连接请求时触发
- connect:客户端连接建立后触发
- read:客户端发送来消息、客户端正常/异常关闭时触发,发送数据超过缓冲区会触发多次
- write:可写事件
处理连接和读事件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
| public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Selector selector = Selector.open();
ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
ssc.configureBlocking(false);
ssc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT, null);
ssc.bind(new InetSocketAddress((8080)));
while (true) {
selector.select();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
ServerSocketChannel channel = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel sc = channel.accept();
sc.configureBlocking(false);
sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ, null);
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
try {
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);
int read = channel.read(buffer);
if (read == -1)
key.cancel();
buffer.flip();
System.out.println(StandardCharsets.UTF_8.decode(buffer));
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("客户端异常断开");
key.cancel();
}
}
iterator.remove();
}
}
}
}
|
处理写事件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
| public class WriteServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
ssc.configureBlocking(false);
Selector selector = Selector.open();
ssc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT, null);
ssc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
while (true) {
selector.select();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
iterator.remove();
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
SocketChannel sc = ssc.accept();
sc.configureBlocking(false);
SelectionKey scKey = sc.register(selector, 0, null);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < 30000000; i++) {
sb.append("a");
}
ByteBuffer buffer = Charset.defaultCharset().encode(sb.toString());
sc.write(buffer);
if (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
scKey.interestOps(scKey.interestOps() + SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
scKey.attach(buffer);
}
} else if (key.isWritable()) {
ByteBuffer buffer =(ByteBuffer) key.attachment();
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
int write = sc.write(buffer);
System.out.println(write);
if (!buffer.hasRemaining()) {
key.attach(null);
key.interestOps(key.interestOps() - SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
}
}
}
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| public class WriteClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
SocketChannel sc = SocketChannel.open();
sc.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080));
int count = 0;
while (true) {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1026 * 1024);
count += sc.read(buffer);
System.out.println(count);
buffer.clear();
}
}
}
|
消息边界问题
utf-8编码下汉字占三个字节,如果没有读全就会产生乱码
处理方式
- 客户端和服务器端约定固定长度的消息格式。缺点:浪费空间
- 在消息中加分隔符,根据分隔符之间的消息长度分配buffer。缺点:慢
- 带头结点,头结点里有后续内容的长度信息,根据长度分配不同长度的buffer。
- TLV格式:Type Length Value
- Http1.1是TLV格式
- Http2.0是LTV格式
多线程优化
好处:
- 充分利用多核cpu资源
- 和耗时较长的任务并行执行
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
| public class MultiThreadServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Thread.currentThread().setName("boss");
ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
ssc.configureBlocking(false);
Selector boss = Selector.open();
ssc.register(boss, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT, null);
ssc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
Worker[] workers = new Worker[2];
for (int i = 0; i < workers.length; i++) {
workers[i] = new Worker("worker-" + i);
}
int index = 0;
while (true) {
boss.select();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = boss.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
iterator.remove();
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
SocketChannel sc = ssc.accept();
sc.configureBlocking(false);
workers[index].register(sc);
index = (index + 1) % workers.length;
}
}
}
}
static class Worker implements Runnable{
private Thread thread;
private Selector selector;
private String name;
private volatile boolean start = false;
private ConcurrentLinkedQueue<Runnable> queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>();
public Worker(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void register(SocketChannel sc) throws IOException {
if (!start) {
selector = Selector.open();
thread = new Thread(this, name);
thread.start();
start = true;
}
queue.offer(() -> {
try {
sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ, null);
} catch (ClosedChannelException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
selector.wakeup();
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
selector.select();
Runnable task = queue.poll();
if (task != null) {
task.run();
}
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
iterator.remove();
if (key.isReadable()) {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
int read = sc.read(buffer);
buffer.flip();
System.out.println(this.name + " : " + Charset.defaultCharset().decode(buffer));
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
|
NIO和BIO对比
stream 和 channel
- 不同:stream不会自动缓冲数据,channel会利用系统提供的发送缓冲区、接收缓冲区
- stream仅支持阻塞API,channel同时支持阻塞、非阻塞API,网络channel可配合selector实现多路复用
- 相同:均为全双工(读写可同时进行)
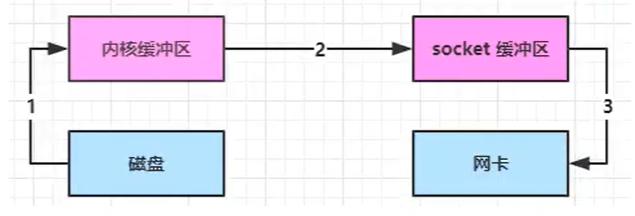
零拷贝
零拷贝指的是不需要把数据拷贝到jvm中
不使用零拷贝数据中共复制了4次,切换用户态/内核态3次
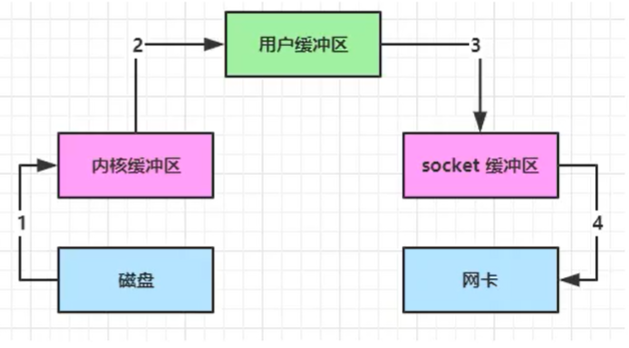
使用DirectBuffer让用户缓冲区和内核缓冲区共用一块内存,减少一次拷贝
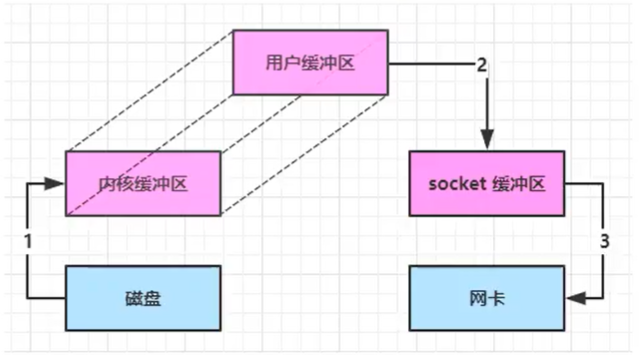
直接从内核缓冲区向客户端的soket缓冲区发数据,减少一次内核切换
零拷贝的有点有:
- 更少的用户态与内核态的切换
- 不利用cpu计算(DMA),减少cpu缓存伪共享
- 零拷贝适合小文件传输
Netty
Netty是 一个异步事件驱动的网络应用程序框架,用于快速开发可维护的高性能协议服务器和客户端。
入门
为何要异步
- 单线程没法异步提高效率,必须配合多线程、多核cpu才能发挥异步的优势
- 异步并没有缩短响应时间,反而有所增加,异步提高的是单位时间内的吞吐量
- 合理进行任务拆分,也是利用异步的关键
Hello World
导包
1
2
3
4
5
| <dependency>
<groupId>io.netty</groupId>
<artifactId>netty-all</artifactId>
<version>4.1.59.Final</version>
</dependency>
|
编写服务器端
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| public class HelloServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ServerBootstrap()
.group(new NioEventLoopGroup())
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<NioSocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println(msg);
}
});
}
})
.bind(8080);
}
}
|
编写客户端
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| public class HelloClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
new Bootstrap()
.group(new NioEventLoopGroup())
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<NioSocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder());
}
})
.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080))
.sync()
.channel()
.writeAndFlush("Hello World");
}
}
|
组件
EventLoop
EventLoop本质是一个单线程执行器(selector + thread),处理channel上发生的事件
EventLoopGroup是一组EventLoop,Channel会绑定其中一个EventLoop,后续这个Channel上的io事件都由此EventLoop来处理(保证io事件处理时的线程安全)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| public class TestEventLoop {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(2);
System.out.println(group.next());
group.next().submit(() -> {
System.out.println("task");
});
group.next().scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
System.out.println("schedule:" + LocalTime.now());
}, 1, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
|
分工:
- group(EventLoopGroup, EventLoopGroup):可以指定两个group来分工,前一个为监听accpet事件,后一个为处理读写事件
- addLast(EventExecutorGroup, String, ChannelHandler):指定EventLoopGroup执行这个处理器;指定处理器名;处理器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| public class EventLoopServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DefaultEventLoopGroup group = new DefaultEventLoopGroup();
new ServerBootstrap()
.group(new NioEventLoopGroup(), new NioEventLoopGroup(2))
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<NioSocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast("handler1", new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
System.out.println(buf.toString(Charset.defaultCharset()));
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);
}
}).addLast(group, "handler2", new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
System.out.println(buf.toString(Charset.defaultCharset()));
}
});
}
})
.bind(8080);
}
}
|
Channel
读写数据的双向通道
主要方法:
- close()
- closeFuture():关闭channel后调用的方法
- pipeline():添加处理器
- write():写入数据到缓冲区
- writeAndFlush():写入数据并刷出
处理连接结果
connect()是非阻塞方法,可以通过sync()当前线程阻塞等待连接建立,或者addListener()添加listener让其他线程等待连接。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| public class EventLoopClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, IOException {
ChannelFuture channelFuture = new Bootstrap()
.group(new NioEventLoopGroup())
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<NioSocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder());
}
})
.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080));
channelFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
future.channel().writeAndFlush("www");
}
});
}
}
|
处理关闭
调用channel.close()关闭channel后,可以用ChannelFuture future = channel.closeFuture();来进行善后处理
sync()同步处理,addListener()异步处理
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
Channel channel = channelFuture.channel();
new Thread(() -> {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
System.out.print(": ");
String msg = sc.nextLine();
if ("q".equals(msg)) {
channel.close();
break;
}
channel.writeAndFlush(msg);
}
}, "input").start();
ChannelFuture future = channel.closeFuture();
future.sync();
System.out.println("善后工作");
|
Future & Promise
继承关系:jdk的Future <– netty的Future <– Promise
- jdk的Future只能同步等待任务结束
- netty的Future可以同步或异步等待任务结束
- Promise不仅有Future的功能,而且脱离了任务独立存在,只作为两个线程间传递结果的容器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| public class TestJdkFuture {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
Future<Integer> future = service.submit(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(1000);
return 1;
}
});
Integer i = future.get();
System.out.println(i);
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| public class TestNettyFuture {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(2);
EventLoop eventLoop = group.next();
Future<Integer> future = eventLoop.submit(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(1000);
return 2;
}
});
future.addListener(new GenericFutureListener<Future<? super Integer>>() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(Future<? super Integer> future) throws Exception {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + ":" + future.get());
}
});
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread());
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| public class TestPromise {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(2);
DefaultPromise<Integer> promise = new DefaultPromise<>(group.next());
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
promise.setSuccess(1);
}).start();
System.out.println(promise.get());
}
}
|
Handler & Pipeline
Pipeline类似流水线,handler为流水线上的一道道工序
handler分为入站、出站两种
- 入站处理器通常是
ChannelInBoundHandlerAdapter的子类,读取客户端数据时触发,也可以向客户端写数据
- 出站处理器通常是
ChannelOutBoundHandlerAdapter的子类,向客户端写回数据时触发,出站处理器的执行顺序适合入站处理器相反的
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| public class TestPipeline {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ServerBootstrap()
.group(new NioEventLoopGroup())
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<NioSocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast("h1", new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter(){
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println(1);
super.channelRead(ctx, msg);
}
});
pipeline.addLast("h2", new ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter(){
@Override
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
System.out.println(2);
super.write(ctx, msg, promise);
}
});
}
})
.bind(8080);
}
}
|
ByteBuf
是对字节数据的封装
优势
- 池化
- 读写指针分离
- 可以自动扩容
- 支持链式调用
- 支持浅拷贝
自动扩容
写入后数据大小未超过512,则选择下一个16的整数倍扩容
写入后数据大小超过512,则选择下一个2^n扩容
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| public class TestByteBuf {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteBuf buf = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer();
System.out.println(buf);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < 300; i++) {
sb.append("a");
}
buf.writeBytes(sb.toString().getBytes());
System.out.println(buf);
}
}
|
选择使用的内存
使用堆内存,写快读慢
1
| ByteBuf byteBuf = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.heapBuffer(10);
|
使用直接内存,写慢读快
1
| ByteBuf byteBuf = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.directBuffer(10);
|
池化
通过池来重用buf,4.1后默认开启
回收
根据实现方式不同,内存回收方式也不同
- UnpooledHeapByteBuf:使用的是JVM内存,只需GC内存回收即可
- UnpooledDirectByteBuf:使用直接内存,需要特殊方法回收
- PooledByteBuf:池化,不用时归还回池中,需要更复杂的规则来回收内存
每个ByteBuf都实现ReferenceCounted接口,通过引用计数方式来判断是否需要回收
如果没释放Buf,在处理器链的尾/头会被释放
切片
将一块ByteBuf切成逻辑上的两块,实际上没有发生数据的拷贝
切片是不能扩容的
原buf释放内存会影响切片,可以通过retain()方法来计数加1从而不会释放内存
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public class TestByteBuf {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteBuf buf = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer(10);
buf.writeBytes(new byte[]{'a', 'b', 'c', 'd'});
ByteBuf f1 = buf.slice(0, 2);
ByteBuf f2 = buf.slice(2, 4);
System.out.println(f1);
System.out.println(f2);
}
}
|
合并
将多块ByteBuf合并成逻辑上的一块,实际上没有发生数据的拷贝
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| public class TestByteBuf {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteBuf buf1 = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer(10);
buf1.writeBytes(new byte[]{'a', 'b', 'c', 'd'});
ByteBuf buf2 = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer(10);
buf2.writeBytes(new byte[]{'a', 'b', 'c', 'd'});
CompositeByteBuf buffer = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.compositeBuffer();
buffer.addComponent(true, buf1);
buffer.addComponent(true, buf2);
System.out.println(buffer);
}
}
|
进阶
粘包 半包
原因:用TCP协议传输数据,由于滑动窗口(缓冲区)传送的时候可能把一段数据分成了几份,导致接收方收到的数据不全(半包),或几条数据一起发过来(粘包);ByteBuf大小也类似
解决方式:
- 定长解码器:
ch.pipline().addLast(new FixedLengthFrameDecode(长度))规定每条消息的长度固定
- 分隔符:
ch.pipline().addLast(new LineBaseFrameDecoder(限定最大长度)),以换行符为分隔符
- LTC解码器:类似报头,如包含内容长度信息等
协议
实例:处理http的入站信息和返回信息
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
| public class TestHttp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NioEventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup();
NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ChannelFuture channelFuture = new ServerBootstrap()
.group(boss, worker)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new HttpServerCodec());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<HttpRequest>() {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, HttpRequest msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println(msg.uri());
DefaultFullHttpResponse response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(msg.getProtocolVersion(), HttpResponseStatus.OK);
byte[] bytes = "<h1>Hello</h1>".getBytes();
response.headers().setInt(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_LENGTH, bytes.length);
response.content().writeBytes(bytes);
ctx.writeAndFlush(response);
}
});
}
})
.bind(8080)
.sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
boss.shutdownGracefully();
worker.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
|
自定义协议
- 要素

消息类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
| @Data
public abstract class Message implements Serializable {
public static Class<? extends Message> getMessageClass(int messageType) {
return messageClasses.get(messageType);
}
private int sequenceId;
private int messageType;
public abstract int getMessageType();
public static final int LoginRequestMessage = 0;
public static final int LoginResponseMessage = 1;
public static final int ChatRequestMessage = 2;
public static final int ChatResponseMessage = 3;
public static final int GroupCreateRequestMessage = 4;
public static final int GroupCreateResponseMessage = 5;
public static final int GroupJoinRequestMessage = 6;
public static final int GroupJoinResponseMessage = 7;
public static final int GroupQuitRequestMessage = 8;
public static final int GroupQuitResponseMessage = 9;
public static final int GroupChatRequestMessage = 10;
public static final int GroupChatResponseMessage = 11;
public static final int GroupMembersRequestMessage = 12;
public static final int GroupMembersResponseMessage = 13;
public static final int PingMessage = 14;
public static final int PongMessage = 15;
public static final int RPC_MESSAGE_TYPE_REQUEST = 101;
public static final int RPC_MESSAGE_TYPE_RESPONSE = 102;
private static final Map<Integer, Class<? extends Message>> messageClasses = new HashMap<>();
static {
messageClasses.put(LoginRequestMessage, LoginRequestMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(LoginResponseMessage, LoginResponseMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(ChatRequestMessage, ChatRequestMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(ChatResponseMessage, ChatResponseMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(GroupCreateRequestMessage, GroupCreateRequestMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(GroupCreateResponseMessage, GroupCreateResponseMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(GroupJoinRequestMessage, GroupJoinRequestMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(GroupJoinResponseMessage, GroupJoinResponseMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(GroupQuitRequestMessage, GroupQuitRequestMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(GroupQuitResponseMessage, GroupQuitResponseMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(GroupChatRequestMessage, GroupChatRequestMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(GroupChatResponseMessage, GroupChatResponseMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(GroupMembersRequestMessage, GroupMembersRequestMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(GroupMembersResponseMessage, GroupMembersResponseMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(RPC_MESSAGE_TYPE_REQUEST, RpcRequestMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(RPC_MESSAGE_TYPE_RESPONSE, RpcResponseMessage.class);
}
}
|
编解码器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
| public class MessageCodec extends ByteToMessageCodec<Message> {
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, Message msg, ByteBuf out) throws Exception {
out.writeBytes(new byte[]{1, 1, 4, 5, 1});
out.writeByte(1);
out.writeByte(0);
out.writeByte(msg.getMessageType());
out.writeInt(msg.getSequenceId());
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
oos.writeObject(msg);
byte[] bytes = bos.toByteArray();
out.writeInt(bytes.length);
out.writeBytes(bytes);
}
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
byte[] magic = new byte[5];
in.readBytes(magic);
byte version = in.readByte();
byte serializerType = in.readByte();
byte messageType = in.readByte();
int sequenceId = in.readInt();
int length = in.readInt();
byte[] bytes = new byte[length];
in.readBytes(bytes, 0, length);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes));
Message message = (Message) ois.readObject();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(magic));
System.out.println(version);
System.out.println(serializerType);
System.out.println(messageType);
System.out.println(sequenceId);
System.out.println(length);
System.out.println(message);
out.add(message);
}
}
|
测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
EmbeddedChannel channel = new EmbeddedChannel(
new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(1024, 12, 4, 0, 0),
new MessageCodec());
LoginRequestMessage message = new LoginRequestMessage("zs", "123456");
channel.writeOutbound(message);
ByteBuf buf = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer();
new MessageCodec().encode(null, message, buf);
channel.writeInbound(buf);
}
}
|











